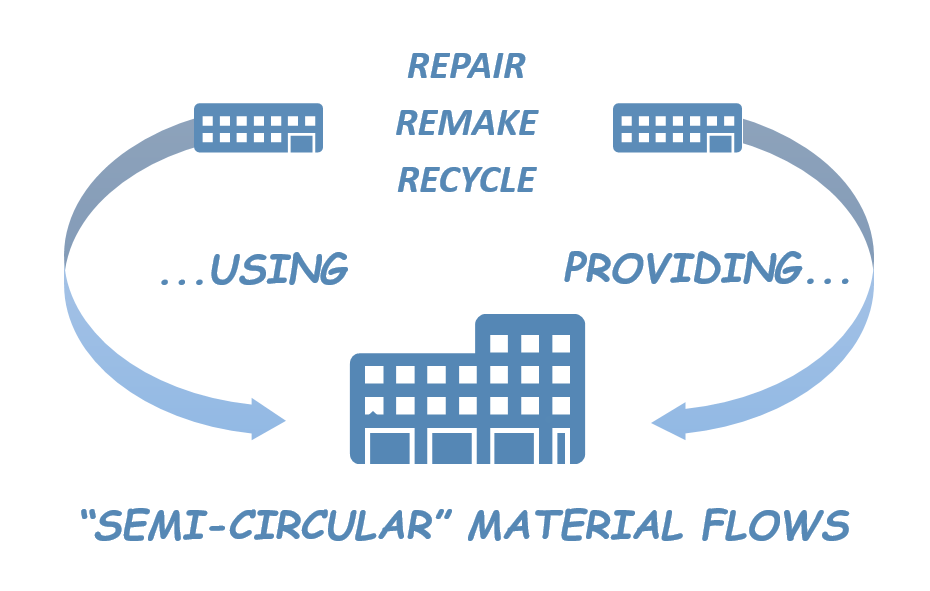
Fashion: from fast and forgettable to slow and sustainable – why purpose-driven brands like Baukjen and Isabella Oliver are choosing circular strategies
Will fast fashion survive the coronavirus lockdown? Big brands are cancelling orders and treating their suppliers as disposable. The time is right for slow, sustainable and circular fashion. We go behind the scenes to look at how the Baukjen and Isabella Oliver brands take a different approach, with beautiful, timeless designs and ethical, more sustainable production. We examine the brands’ circular and partnership approaches through the lens of Permaculture.